Java Aqs
Java Aqs
March 21, 2025
abstract queued synchronizer 是啥?
AQS is an abstract class that provides a skeleton for
managing thread contention,queuing, andstate synchronization. It uses aFIFO wait(sync) queueto manage threads waiting for access to a shared resource and anatomic integer (state)to track the synchronizer’s status (e.g., locked/unlocked, available permits).
- lock
- wait queue 不包括伪头,为啥需要?因为被唤醒的节点是前一个节点唤醒的。
- LockSupport#park 等待
- LockSupport#unpark 唤醒
AQS 数据结构
/**
* Head of the wait queue, lazily initialized. Except for
* initialization, it is modified only via method setHead. Note:
* If head exists, its waitStatus is guaranteed not to be
* CANCELLED.
*/
private transient volatile Node head; // 等待队列的 head
/**
* Tail of the wait queue, lazily initialized. Modified only via
* method enq to add new wait node.
*/
private transient volatile Node tail; // 等待队列的 tail
/**
* The synchronization state.
*/
private volatile int state; // 同步状态, 这就是所谓的 lock
/**
* The current owner of exclusive mode synchronization.
*/
private transient Thread exclusiveOwnerThread;//继承自 AbstractOwnableSynchronizerNode 数据结构
组成双向链表,在之上构建等待队列
volatile int waitStatus; // 下一个 Node 等待状态
volatile Node prev; // 前驱节点
volatile Node next; // 后继节点
volatile Thread thread; // 入队等待的线程RentrantLock.lock 整体概览
FairSync.lock 分析
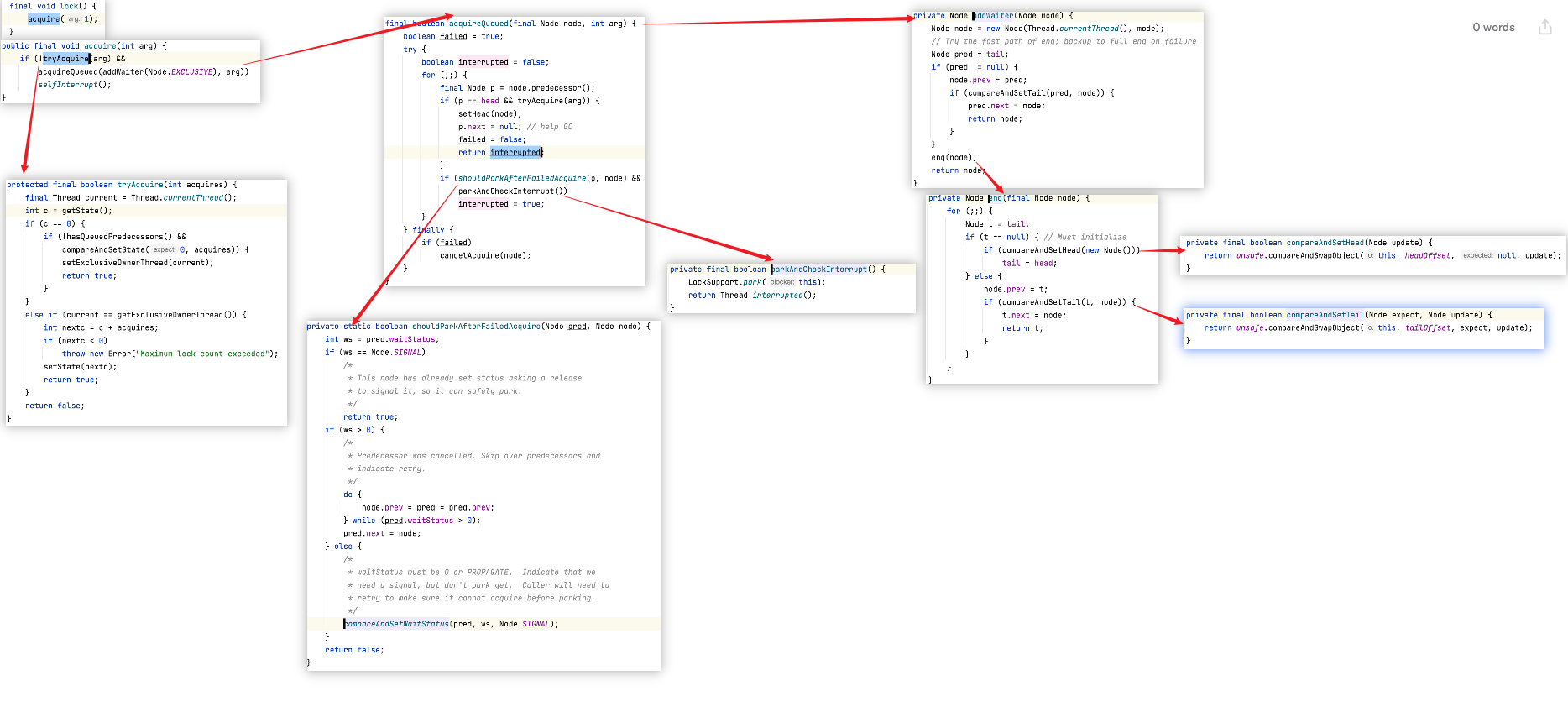
acquire(1) 分析
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.java
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}tryAcquire若返回为 true, 表明获取 lock 成功, !tryAcquire 为 false, 获取 lock 流程结束。这就是 Fast Path。tryAcquire若返回为 false, 表明获取 lock 失败, 为啥失败, 因为有其他线程获取了, 但是还没有释放。这就是 Slow Path。- 流程进入
addWaiter, 也就是当前线程去排队等待获取 lock。
- 流程进入
tryAcquire 分析
ReentrantLock.java
/**
* Fair version of tryAcquire. Don't grant access unless
* recursive call or no waiters or is first.
*/
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); // 当前申请获取锁的线程
int c = getState(); // lock 的状态
if (c == 0) { // lock 是 unlock 状态
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() && // 看一下队列中是不是已有在等待获取锁的线程,这就是所谓公平的体现,FIFO
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) { // 没有在等待获取锁的线程, 获取锁,这里 CAS 可能会失败
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current); // 本线程持有这个锁
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) { // 该线程已经持有了锁
int nextc = c + acquires; // 直接改变状态,这就是所谓可重入的意思,已经获取锁的线程,可以再次获取该锁
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded"); // 这里可能会抛异常
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}addWaiter 分析
线程获取锁失败, 到阻塞队列去排队。这里是 addWaiter(null, 1)
ReentrantLock.java
/**
* Creates and enqueues node for current thread and given mode.
*
* @param mode Node.EXCLUSIVE for exclusive, Node.SHARED for shared
* @return the new node
*/
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure
Node pred = tail;
if (pred != null) { // 说明队列不空,直接加到队尾
node.prev = pred; // 设置 node 前驱
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) { // AQS 设置该节点为新的 tail
pred.next = node; // 设置 pred 后继
return node; // 返回包装申请锁的线程的 Node 节点
}
}
enq(node); // 说明队列为空, enq 返回 node 的前驱节点
return node; // 返回包装申请锁的线程的 Node 节点
}enq 入队分析
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.java
/**
* Inserts node into queue, initializing if necessary. See picture above.
* @param node the node to insert
* @return node's predecessor
*/
private Node enq(final Node node) {
for (;;) {
Node t = tail;
if (t == null) { // Must initialize 队尾为空,说明等待队列一个节点都没有
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node())) // 设置等待队列伪队头,其实就是为了给需要唤醒的节点准备前置节点。
tail = head; // 设置队尾
} else {
node.prev = t; // 设置该节点的前置节点
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) { // 该节点设置成队尾
t.next = node;
return t;
}
}
}
}addWaiter 图示
链表,还是画一画图,理解的更好
- tail == null, 等待队列里一个等待的线程 Node 也没有
- enq 入队, 创建一个 Node 节点,作为 head, 再添加要获取锁的节点
- tail != null, 等待队列里已经有等待的线程 Node 了
- 直接添加到等待队列队尾
acquireQueued 分析
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.java
/**
* Acquires in exclusive uninterruptible mode for thread already in
* queue. Used by condition wait methods as well as acquire.
*
* @param node the node
* @param arg the acquire argument
* @return {@code true} if interrupted while waiting
*/
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) { // 注意是循环
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) { // 【是等待队列的第一个 && tryAcquire】 , true 表明获取了锁
setHead(node); // 本节点设置成 head, 旧的 head 出队
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && // 锁已被其他线程获取, 会走到这里
parkAndCheckInterrupt()) // 停止运行,去 sleep
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}acquireQueued for 循环退出两种情况
- 当前节点是等待队列第一个 && tryAcquire 成功获取了锁
- tryAcquire 抛出了 Error(超出了锁的最大可重入次数😂), finally 的 failed 逻辑会执行 cancelAcquire
acquireQueued 两轮循环线程进入 sleep 分析
第一个等待节点添加时需要两轮 for 循环
- 第 1 轮 for 循环
- pred 的 waitStatus = 0, 此时
shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire将 pred 节点的 waitStatus 设置为 -1(Signal) 代表 pred 节点需要唤醒该节点。返回 false 进入第二轮循环。
- pred 的 waitStatus = 0, 此时
- 第 2 轮 for 循环
- pred 的 waitStatus = -1,
shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire返回 true。 parkAndCheckInterrupt中调用LockSupport.park当前线程,停止在此处。获取不到锁,那就去 sleep。
- pred 的 waitStatus = -1,
cancelAcquire 分析
/**
* Cancels an ongoing attempt to acquire.
*
* @param node the node
*/
private void cancelAcquire(Node node) {
// Ignore if node doesn't exist
if (node == null)
return;
node.thread = null; // 取消线程
// Skip cancelled predecessors 跳过取消的节点
Node pred = node.prev;
while (pred.waitStatus > 0)
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
// predNext is the apparent node to unsplice. CASes below will
// fail if not, in which case, we lost race vs another cancel
// or signal, so no further action is necessary.
Node predNext = pred.next;
// Can use unconditional write instead of CAS here.
// After this atomic step, other Nodes can skip past us.
// Before, we are free of interference from other threads.
node.waitStatus = Node.CANCELLED;
// If we are the tail, remove ourselves. 队尾
if (node == tail && compareAndSetTail(node, pred)) { // expect update
compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, null); // node expect null
} else {
// If successor needs signal, try to set pred's next-link
// so it will get one. Otherwise wake it up to propagate.
// 不是队尾,也就是等待队列的其他节点
int ws;
if (pred != head && // 不是等待队列中第一个节点
((ws = pred.waitStatus) == Node.SIGNAL ||
(ws <= 0 && compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL))) &&
pred.thread != null) { // pred.thread != null 表示前驱节点有线程在等待获取锁
Node next = node.next;
if (next != null && next.waitStatus <= 0) // 取消节点有后继节点 next 且后继节点 waitStatus <= 0
compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, next); // pred 设置新的 next 节点
} else {
// 取消等待的节点是等待队列中的第一个节点, 叫醒后继节点
unparkSuccessor(node);
}
node.next = node; // help GC
}
}if 为 true 判断分析
为了将
取消节点的前驱节点和取消节点的后继节点进行链接
if (pred != head &&
((ws = pred.waitStatus) == Node.SIGNAL ||
(ws <= 0 && compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL))) &&
pred.thread != null) - pred != head 为 true 表示取消节点不是等待队列中第一个节点
- ((ws = pred.waitStatus) == Node.SIGNAL || (ws <= 0 && compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL))) 为 true
- (ws = pred.waitStatus) == Node.SIGNAL 为 true, 前驱节点的 waitStatus 为 -1
- (ws <= 0 && compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL)) 为 true
- ws <= 0 为 true, 前驱节点的 waitStatus 为 0, 那就 compareAndSetWaitStatus 前驱节点的 waitStatus 为 -1
- compareAndSetWaitStatus 返回为 true, 设置前驱节点的的 waitStatus 为 -1 成功
- pred.thread != null 为 true 前驱节点有等待的线程
shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire 分析
为即将被 block 的线程,设置前驱节点的 waitStatus 为 -1, 表示下一个节点需要被唤醒
/**
* Checks and updates status for a node that failed to acquire.
* Returns true if thread should block. This is the main signal
* control in all acquire loops. Requires that pred == node.prev.
*
* @param pred node's predecessor holding status
* @param node the node
* @return {@code true} if thread should block
*/
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
int ws = pred.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)
/*
* This node has already set status asking a release
* to signal it, so it can safely park.
*/
return true;
if (ws > 0) { // 线程取消了获取锁, 找到一个没有取消的
/*
* Predecessor was cancelled. Skip over predecessors and
* indicate retry.
*/
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
pred.next = node;
} else {
/*
* waitStatus must be 0 or PROPAGATE. Indicate that we
* need a signal, but don't park yet. Caller will need to
* retry to make sure it cannot acquire before parking.
*/
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL); // 设置前驱节点的 waitStatus 为 -1
}
return false;
}parkAndCheckInterrupt 分析
线程状态进入 waiting 的重要逻辑
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.java
/**
* Convenience method to park and then check if interrupted
*
* @return {@code true} if interrupted
*/
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
LockSupport.park(this); // 调用线程执行到这里就不再继续向下执行了, 这是理解线程 waiting 的关键
return Thread.interrupted(); // 线程被唤醒后才会 return, 执行下一轮的 acquireQueued
}FairSync.unlock 分析
release 分析
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.java
/**
* Releases in exclusive mode. Implemented by unblocking one or
* more threads if {@link #tryRelease} returns true.
* This method can be used to implement method {@link Lock#unlock}.
*
* @param arg the release argument. This value is conveyed to
* {@link #tryRelease} but is otherwise uninterpreted and
* can represent anything you like.
* @return the value returned from {@link #tryRelease}
*/
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) { // 释放锁
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0) // waitStatus 为 -1, 表明下一个节点需要被唤醒
unparkSuccessor(h); // 唤醒 head 节点后的节点,也就是等待队列中第一个节点
return true;
}
return false;
}tryRelease 分析
- 该方法可能抛出异常
AbstractOwnableSynchronizer.java
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
int c = getState() - releases;
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread()) // 是不是持有该锁的线程在 release
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
if (c == 0) { // 已完全释放,因为可以重入
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
setState(c); // lock 设置成 unlock 状态,也就是 0,这就是所谓的释放锁
return free;
}unparkSuccessor 分析
AbstractOwnableSynchronizer.java
/**
* Wakes up node's successor, if one exists.
*
* @param node the node
*/
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
/*
* If status is negative (i.e., possibly needing signal) try
* to clear in anticipation of signalling. It is OK if this
* fails or if status is changed by waiting thread.
*/
int ws = node.waitStatus;
if (ws < 0) // Signal = -1
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
/*
* Thread to unpark is held in successor, which is normally
* just the next node. But if cancelled or apparently null,
* traverse backwards from tail to find the actual
* non-cancelled successor.
*/
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
if (s != null)
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread); // 唤醒这个线程,该线程在 park 处返回,接着执行 acquireQueued 的 for 循环,去获取锁。
}References
Last updated on


